
Bhakti Movement
Medieval devotional movement emphasizing personal love for God that transformed Indian spirituality, challenging caste barriers and inspiring regional literature.
Discover the philosophies, movements, and cultural concepts that defined Indian thought

Medieval devotional movement emphasizing personal love for God that transformed Indian spirituality, challenging caste barriers and inspiring regional literature.


Form of nonviolent resistance developed by Mahatma Gandhi, combining truth and firmness to achieve social and political change through moral force.


The ancient Indian philosophical and ethical principle of non-violence toward all living beings, foundational to Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, and famously adopted by Mahatma Gandhi

Ancient Hindu system dividing life into four stages (Brahmacharya, Grihastha, Vanaprastha, Sannyasa) for spiritual and social development across the lifespan.


Ancient Indian classical dance form from Tamil Nadu, combining expressive storytelling with rhythmic precision through bhava, raga, and tala.

Classical music tradition of South India with ancient roots, characterized by intricate ragas, devotional themes, and a rich compositional heritage spanning centuries.
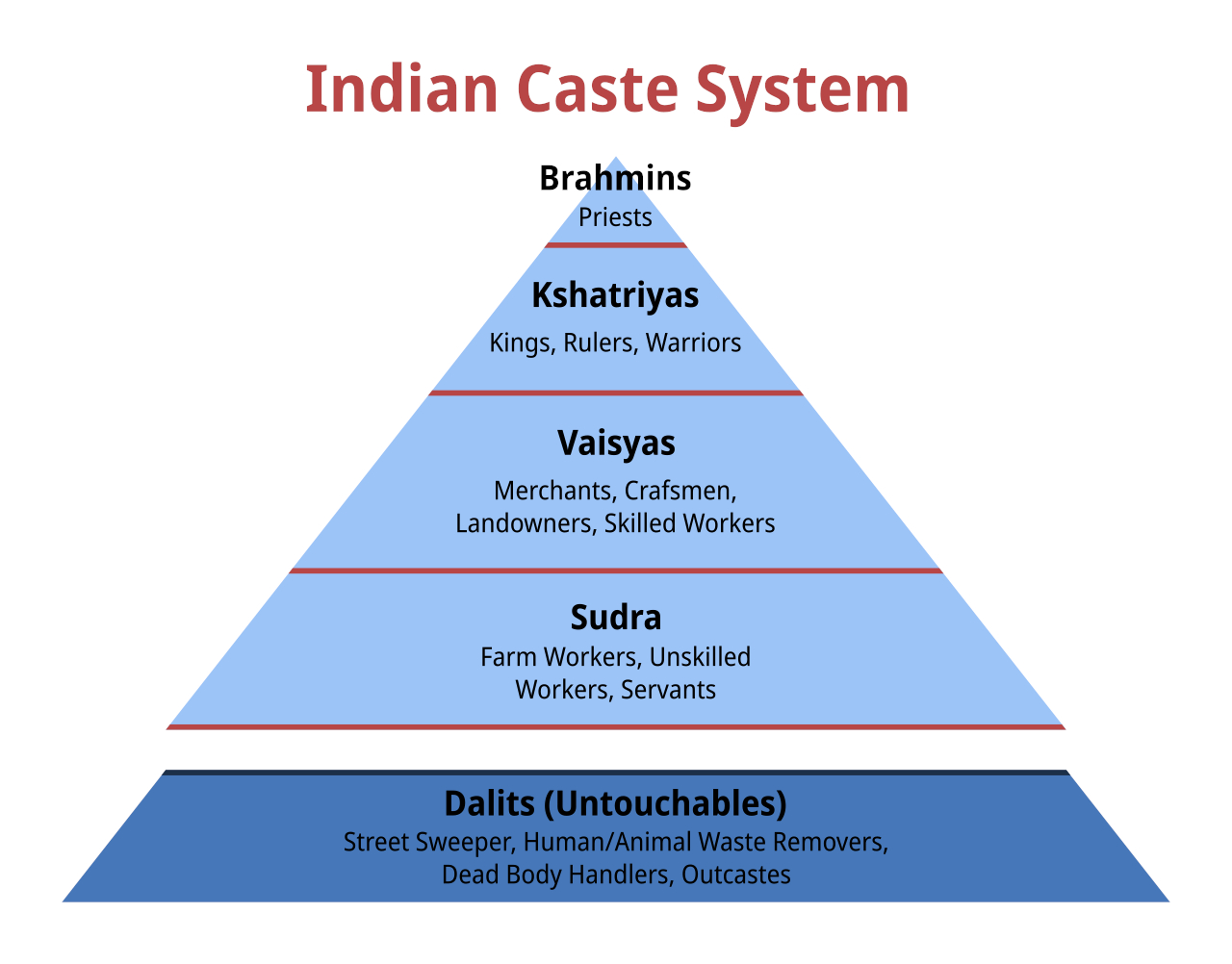
Ancient social stratification system that has profoundly shaped Indian society, organizing communities into hierarchical hereditary groups based on occupation and ritual purity.


Ancient art music tradition of northern India and Pakistan, characterized by raga-based improvisation, deeply rooted in spiritual and cultural heritage.



India's system of local self-government through village councils, constitutionally empowered since 1992 to decentralize governance and promote grassroots democracy.

Puja is a devotional worship ritual in Hinduism involving offerings and prayers to deities, practiced in homes and temples across India for millennia.



Indian independence movement strategy promoting domestic goods and boycotting British products, crucial in nationalist resistance from 1905-1947.


Ancient Hindu social classification system dividing society into four hierarchical groups: Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras, described in Vedic texts.
